Dental Journals
Genesis Publications

Breaking Barriers in Maxillary Rehabilitation
Rehabilitating an atrophied maxilla is a significant challenge in implant dentistry because of the limited bone volume and density in this area.
The maxilla often has reduced bone height and width from tooth loss, periodontal disease, or trauma, which can make placing conventional implants difficult. Additionally, the bone in the maxilla is typically less dense than the mandible, which can affect the implant’s initial stability and the biological process of osseointegration.
Traditionally, treatments for an atrophied maxilla include bone augmentation techniques such as sinus floor elevation, onlay grafting, and guided bone regeneration. While effective………
Genesis Publications
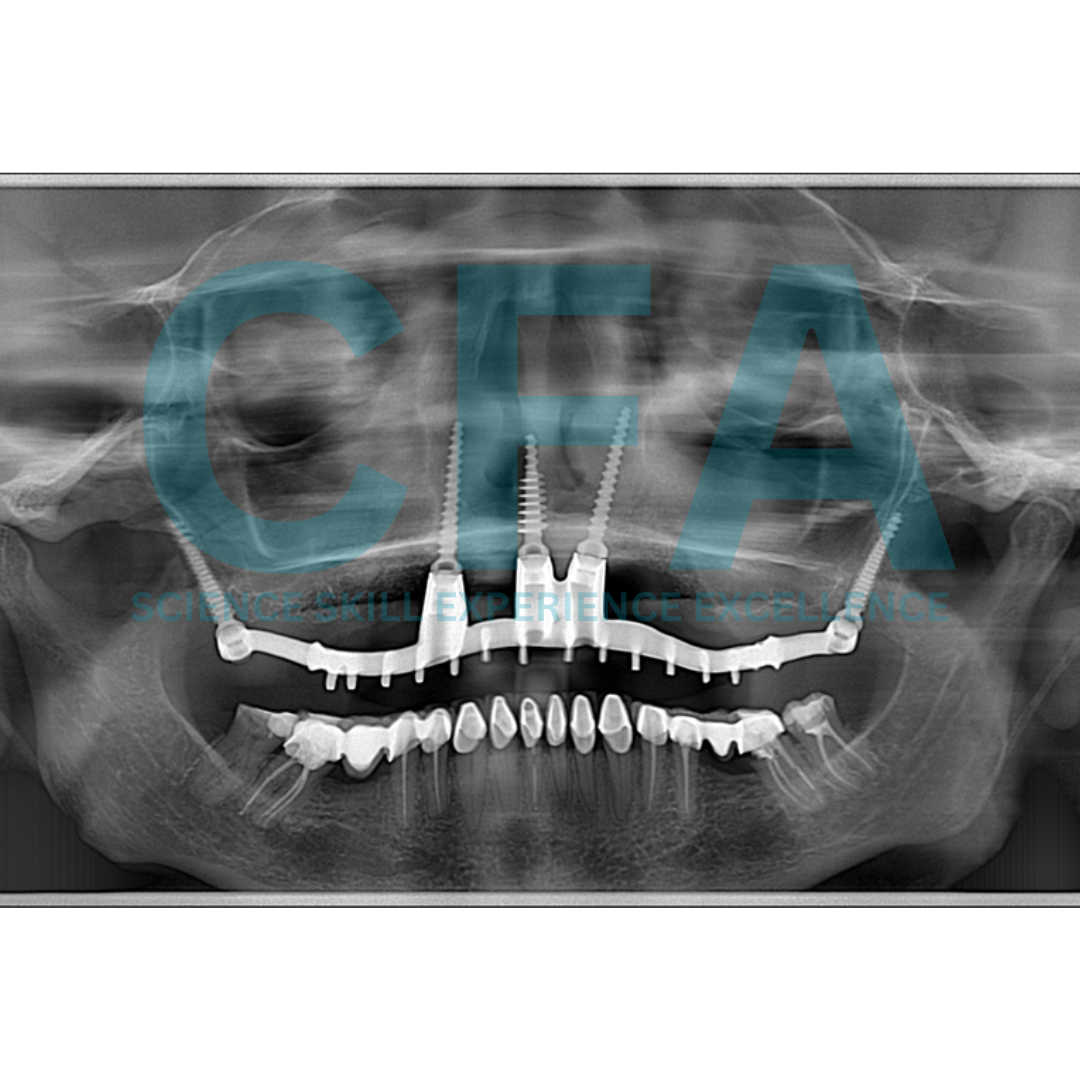
The Bone Truss Bridge (BTB) approach for Atrophic Maxilla Rehabilitation
The Bone Truss Bridge (BTB) concept represents a novel and promising approach for dental implant rehabilitation in the atrophic maxilla. It offers a minimally invasive alternative to traditional two-piece implants with angulated abutments. Additionally, the milled metal frame with angulated screw channels allows for easy retrievability in case of complications.
The BTB approach demonstrated high patient satisfaction due to reduced treatment time and a less invasive procedure compared to traditional methods.
The presented case studies highlight successful outcomes. Further research, validation, and broader clinical applications will be essential to further establish the role of the BTB approach in the future of implant dentistry.
MAR Dental Sciences & Oral Rehabilitation (2023)

Minimal Invasive Approaches to Maxillary Atrophy
The rehabilitation of an atrophied maxilla presents a complex, multi-faceted challenge for the dental professional1- 3. A variety of strategies have been developed over the years, each with its unique set of benefits and drawbacks. The more invasive techniques, while often effective, involve a greater level of surgical trauma, higher cost, longer recovery times, and a higher risk of complications 4- 7. On the other hand, minimal invasive approaches offer several advantages, including shorter healing periods and less surgical morbidity, albeit with their own set of challenges 8 -11. Among these, the use of pterygoid implants and the transnasal approach, when applied with specific implants, may allow for early loading, providing patients with a functional, aesthetic, and stable oral rehabilitation within 2-3 weeks 5,10. This paper present two cases that illustrate the application and effectiveness of these minimally invasive strategies
Journal of Oral Medicine and Dental Research
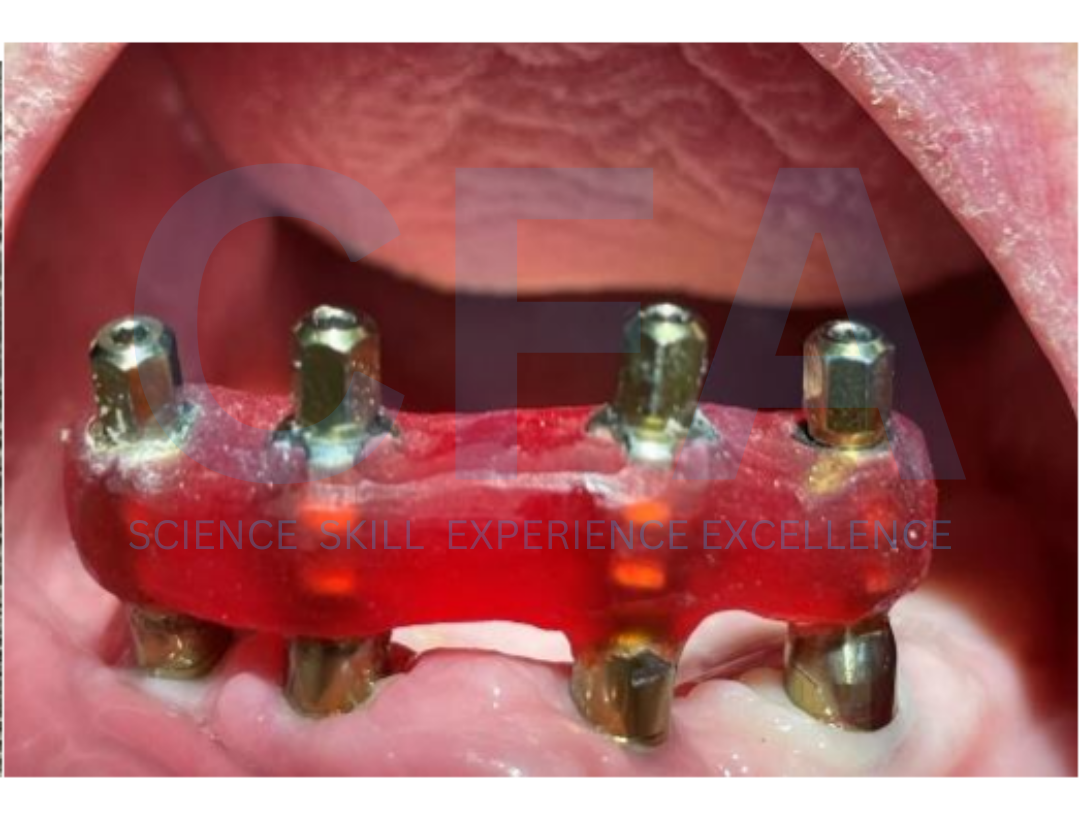
Treatment Modalities for Overdentures on Screw-Retained Bars on Implants
Full-arch rehabilitation for the maxilla and mandible using fixed implant-supported prostheses offers superior function, prosthetic stability, and enhanced quality of life. However, these treatments are often cost-prohibitive, making them inaccessible for many patients [1,2].
Implant overdentures present a more affordable alternative, providing improved function and stability with the use of two or more implants for retention. Unlike fixed full-arch restorations, implant overdentures are relying primarily on soft-tissue for support and can be removed by the patient for
routine hygiene purposes [3-5].
Juniper Publishers
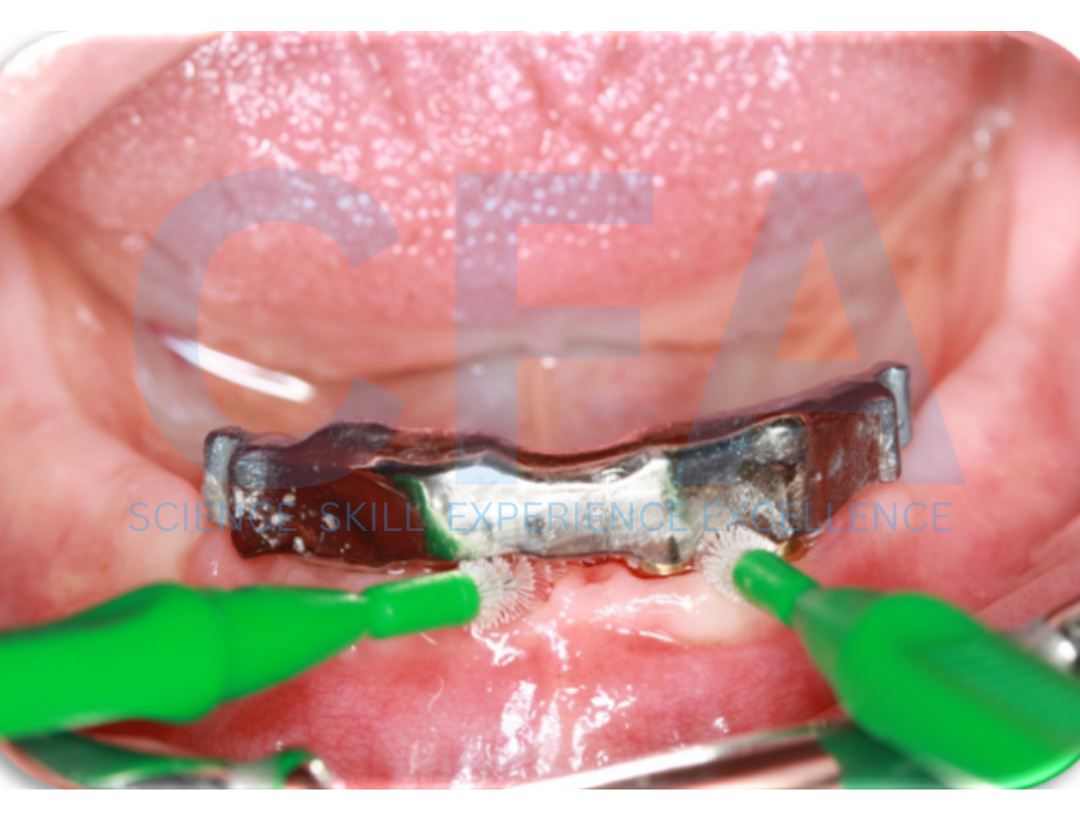
Minimal Invasive Modality for Full Rehabilitation of Edentulous Mandible with One-Piece Implants in Elderly Patients
The use of conventional implants in the rehabilitation of edentulous space has been discussed extensively in the literature [1-4]. However, conventional implant systems may be limited or inapplicable in restoring some edentulous spaces due to various anatomical reasons. One of such reason is insufficient space between adjacent edentulous teeth for the use of a conventional implant which makes implant placement impossible [4,5-7]. In these situations, an alternative implant system for the restoration of such cases is required. The One-Piece implants help in restoring edentulous spaces that previously cannot be restored with conventional implants; it also encourages the use of minimally invasive surgical techniques which encourage maximum tissue preservation [8,9]
BIO MEDICAL
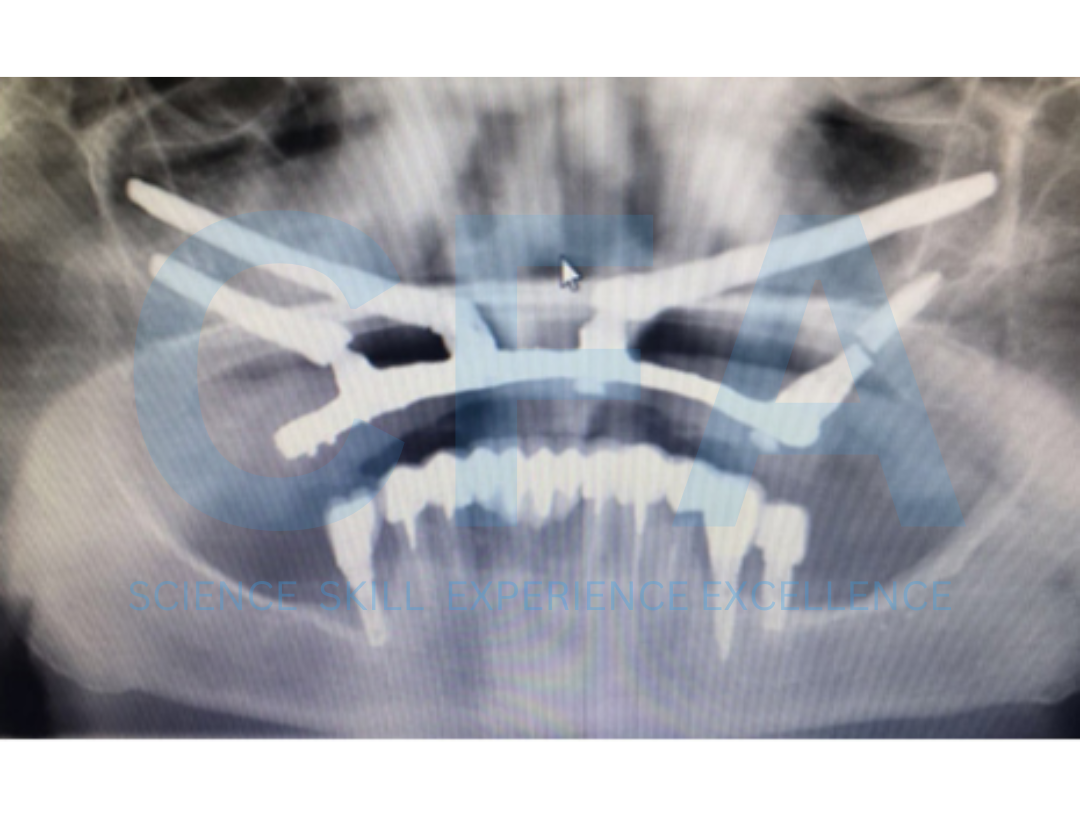
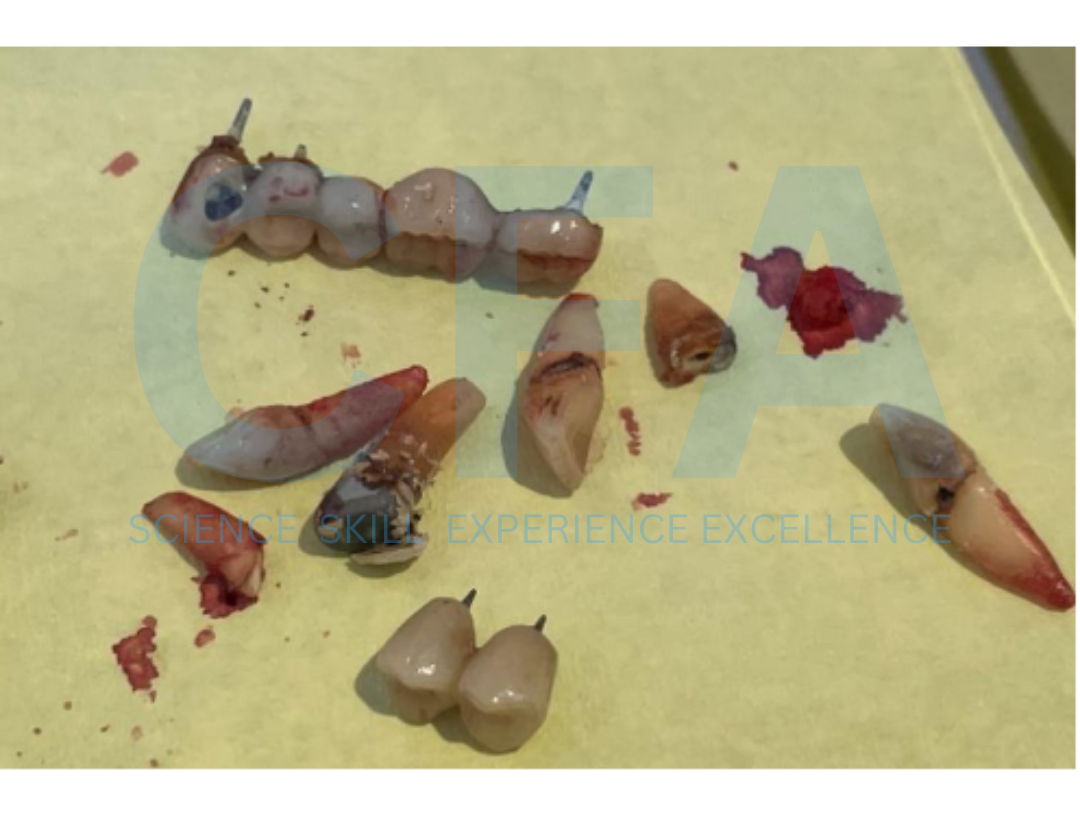
Retreatment of a Failed Quad Zygoma Implant Procedure with Cortically Fixed at once Hybrid Plates: Case Report
Restoration of a severely edentulous arch poses an enormous
challenge to the dentist more so in the maxillary region where
various anatomical structures reduce the option for extensive
surgery. Bone augmentation may be required to enable placement of a sufficient number and length of implants to support an implant prosthesis [1,2]. Retreatment of failed implant further complicates the existing problem because of further loss of bone height associated with loss implant and the presence of scar tissue in the previous operated and implant site which make reoperation difficult. Zygomatic Implants have been used to provide support for oral rehabilitation where there has been a substantial amount of
bone loss from the upper jaw due to resorption or implant failure [3,4].
Irish Dental Magazine
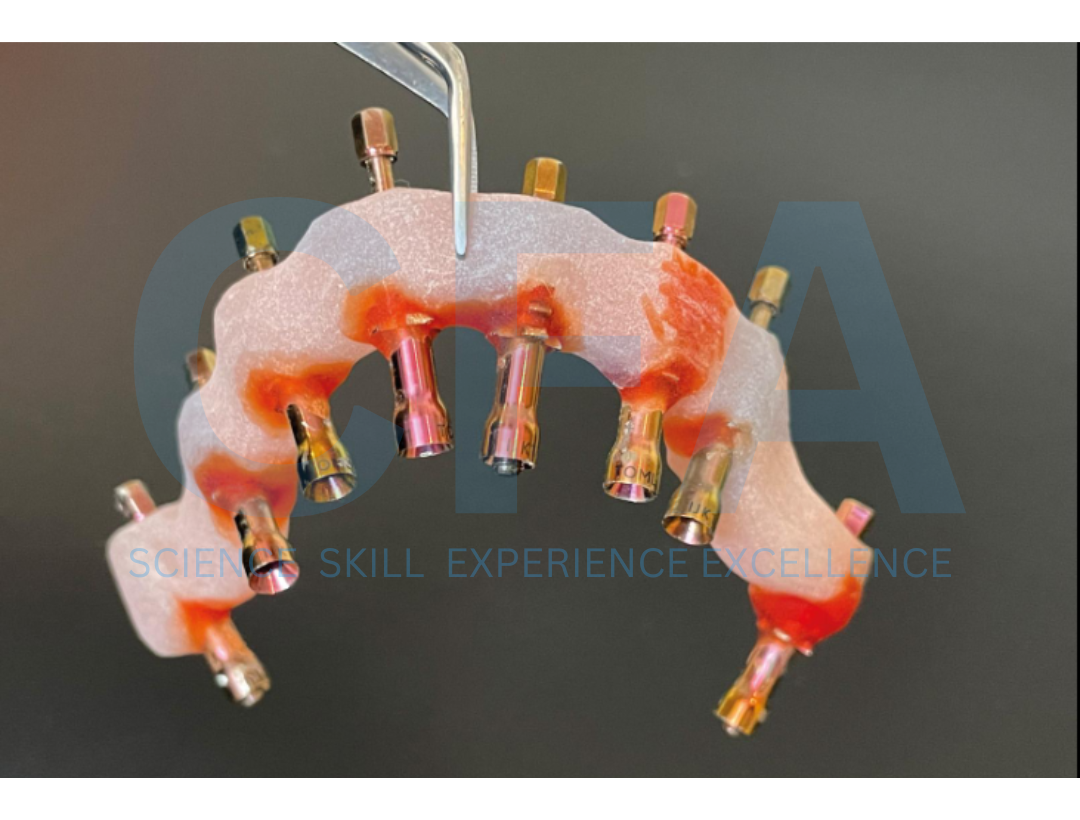
Minimally invasive treatment options in the atrophied bone
The rehabilitation of an atrophied maxilla presents a complex, multi-faceted challenge for the dental professional1- 3. A variety of strategies have been developed over the years, each with its unique set of benefits and drawbacks. The more invasive techniques, while often effective, involve a greater level of surgical trauma, higher cost, longer recovery times, and a higher risk of complications 4- 7. On the other hand, minimal invasive approaches offer several advantages, including shorter healing periods and less surgical morbidity, albeit with their own set of challenges 8 -11. Among these, the use of pterygoid implants and the transnasal approach, when applied with specific implants, may allow for early loading, providing patients with a functional, aesthetic, and stable oral rehabilitation within 2-3 weeks 5,10. This paper present two cases that illustrate the application and effectiveness of these minimally invasive strategies
RESEARCH GATE
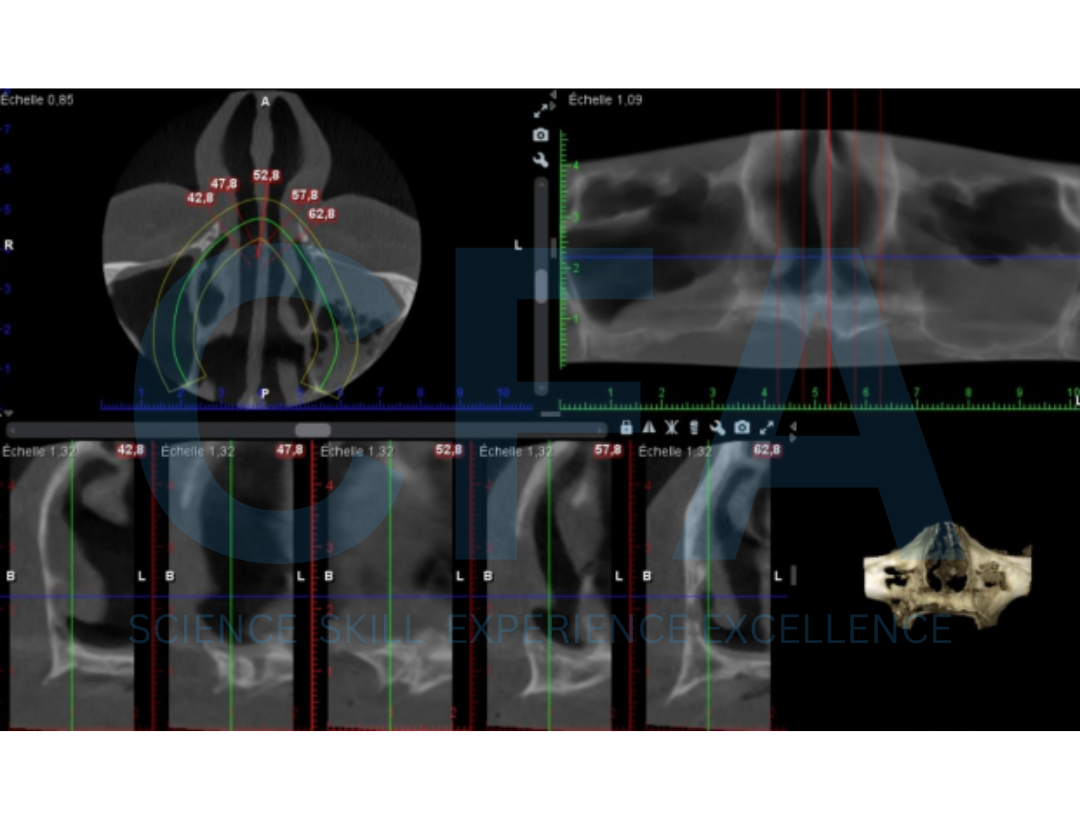
A Novel Technique for the Treatment of Severely Atrophied Maxilla with Immediate Dental Implant Loading
International Journal of Case Reports & Short Reviews
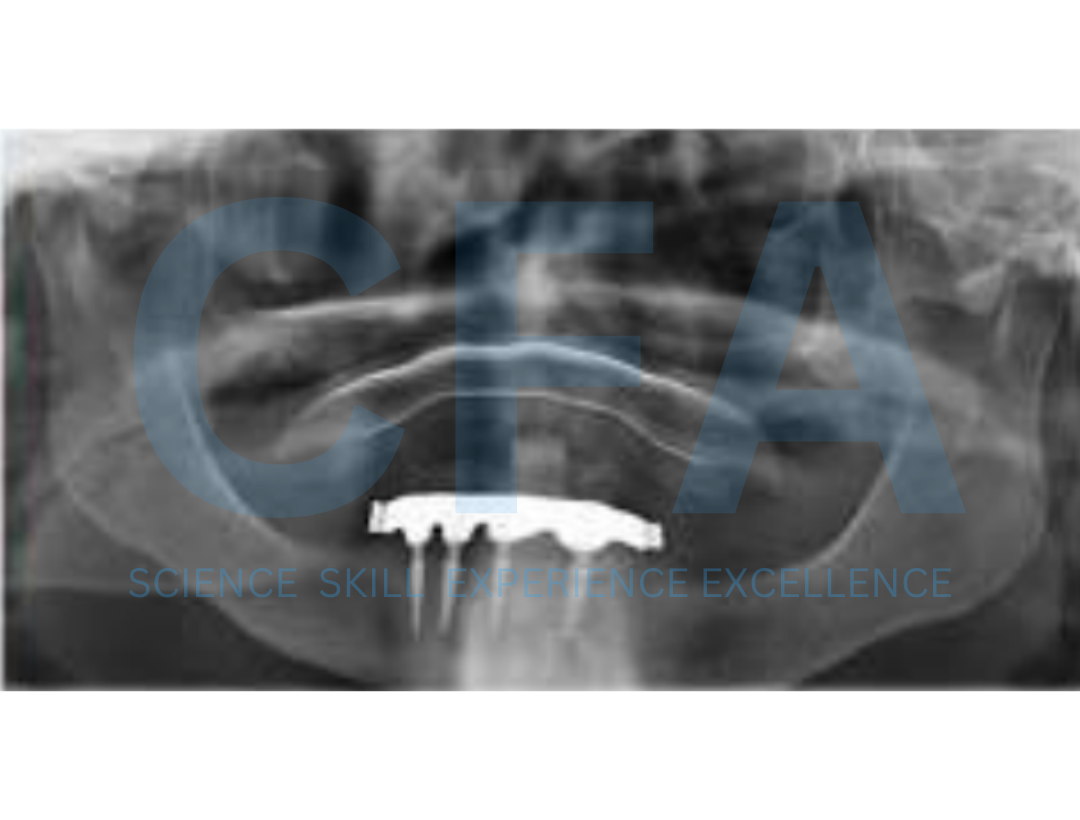
Minimal Invasive Concept for the Rehabilitation of Edentulous Jaw with One-piece Implants
The use of conventional implants in the rehabilitation of
edentulous space has been discussed extensively in the literature [1-4]. However, conventional implant systems may be limited or inapplicable in restoring some edentulous spaces due to various anatomical reasons. One of such reason is insuffi cient space between adjacent edentulous teeth for the use of a conventional implant e.g. regular Platform implants (3.5 – 4.5 mm diameter) or Wide Diameter implants (usually > 4.5 mm in diameter) which makes implant placement impossible [5-7,8,4]. In these situations, an alternative implant system for the restoration of such cases is required.

